Diamond Sourcing
Diamonds are made of carbon and naturally found from within the Earth's surface. Diamonds are crystallized carbon that, with the application of natural heat and pressure from within the Earth's surface, form into one of the Earth's hardest substances. It takes millions of years for diamonds to form and a miner must sift through 250 tons of rock to unearth 1.00ct of diamond. There is no set location where diamonds are unearthed or mined. Diamonds have been found in every region, climate and location around the world, including the United States. Originally, Africa was the central hub where almost 90% - 100% of the Earth's diamonds were uncovered and mined. Today, less than 50% of the Earth's diamonds come from African mines. Diamonds are mined from African nations, Russia, Canada, Australia, India and Brazil. Mines are both privately owned entities and government sponsored enterprises. Because of the value of diamonds, their mining is tightly controlled globally.
What are Conflict Diamonds?
Diamonds have been a source of controversy in trade and conflict because they are small and possess a lot of value. Diamonds are not the only source of conflict, however. All the metals and minerals used in things like cell phone chips have also contributed to conflicts. Nonetheless, diamonds, when used to fuel civil unrest or wars, are considered conflict diamonds. Today, conflict diamonds account for less than 0.1% of diamonds in the global jewelry industry.
Diamonds mined or sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo, Zimbabwe, Angola, Sierra Leone, and Liberia are conflict diamonds. Other African nations produce high quality diamonds and abide by ethical, democratic practices. For generations, diamonds have been at the source of community building and job creation. They support many people's livelihoods across the globe. It is our utmost responsibility to protect and preserve ethical practices in order to sustainably build communities and not ruin them with conflicted diamonds.
Diamond sourcing goes beyond just conflict. We genuinely believe in additional practices that go the extra mile. These include fair trade suppliers only and cruelty free diamonds that don't harm animals or the environment in the mining process. Conflicts don't just involve people. It is more important than ever that we do not leave an ecological footprint, especially when engagement rings symbolize nature and natural emotions such as love and togetherness. Our ethically sourced diamonds have the additional protection of knowing we go beyond conflict free and and source responsibly. Everyone has to do their part, and we make the extra effort to do ours.
Kimberley Process
In order to combat conflict diamonds and to standardize mining practices, the international community established a no tolerance policy against the use of conflict diamonds. This was known as the Kimberley Process, established in 2000. In a nutshell, this Process requires the issuance and authorization of a certificate for each mined rough diamond. Today, over 74 governments have adopted the accords to protect against conflict diamonds.Countries have used this as an opportunity to safely mine diamonds, secure their origins and invest revenues in building schools, hospitals and infrastructure. Countries such as Australia, Botswana, Canada, Namibia, Russia, South Africa and Tanzania have greatly benefited from safe and secure mining practices.
With Clarity ensures that all diamonds sourced from its manufacturers are within the proper practices of the Kimberley Process. We work directly with these manufacturers to ensure they meet the standard of ethics above and beyond the Kimberley Process.
With Clarity is committed to the highest level of ethical responsibility. We understand that the diamond you purchase is a symbol of love and commitment. For this reason, we ensure that every diamond we offer is not tainted by conflict or human rights abuses. We work to enforce the strictest standards set forth by the Kimberley Process and United Nations Resolutions. At With Clarity, we're proud that the distribution of our jewelry, from mine to market, adheres with all international laws and human rights policies. With supplier relationships that span generations, we have transparency into the operations and sourcing of our suppliers. We only work with reputable suppliers who value conflict-free sourcing and ethical business practices.
With Clarity Policy & Conflict Diamonds

With Clarity's ethical diamond policies and practices focus on 5 major areas of mining and sourcing. We specialize in fair trade diamonds to ensure all best practices of internaitonal business and commerce are met.
1. Financing wars: With Clarity works with suppliers to source diamonds only from mines outside conflict zones where diamonds can be used to fund civil and religious wars. Diamonds are intended to be a commitment of love. War is the opposite and so we ensure our suppliers have origin verification that proves no rough diamond was acquired from an illegitimate source in a war torn region.
2. Human Rights Abuses: It is imperative the mining practices are safe and ethical without the abuse of human rights and civil liberties. With Clarity suppliers source directly from mining companies that abide by local laws in nations that are known for democratic and fair labor law practices. Our diamonds are fair trade.
3. Environmental safety: Of equal importance, it is our responsibility to leave as small a footprint on the Earth as possible so it can be protected for future generations. This is particularly relevant with diamond mining as 250 tons of rock are required to discover a single carat of diamond. We work with manufacturers and miners that deploy the best technology to avoid environmental sacrifice. Cutting corners is not our practice.
4. Fair Labor: Diamond have been a pillar of many communities. They provide stable jobs, fair wages and opportunities that otherwise would never exist. This is true in both manufacturing and mining. With Clarity's suppliers employ large communities of people and follow local fair labor practices and many are even governed by wage and labor unions for employee protection.
5. Community Development: diamonds finance schools, hospitals and infrastructure to many remote locations around the world. Our miners and manufacturers believe in giving back and donate profits and opportunities to communities that allow people to grow personally, financially and professionally.
6. Origin Verification: we verify the origin of every one of our diamonds. While GIA cannot discern a diamond's origin, we verify it with each manufacturer and make the information readily available. If you'd like to know more about your potential With Clarity diamond, just ask!
Diamond Origins
Many changes have occurred in diamond sources within the diamond industry over the last 20 years or so. The diamond trade is no longer monopolized by just a few large companies today there are many smaller diamond mines that are significant players in the diamond trade. Traditionally South Africa was the largest exporter of diamonds to the rest of the world, but within the last 20 years, countries outside of Southern Africa have discovered that they also share this resource. This has allowed other jewelers a foothold in the market and has resulted in the decline of huge brand names in the diamond jewelry business.
Diamond Sources
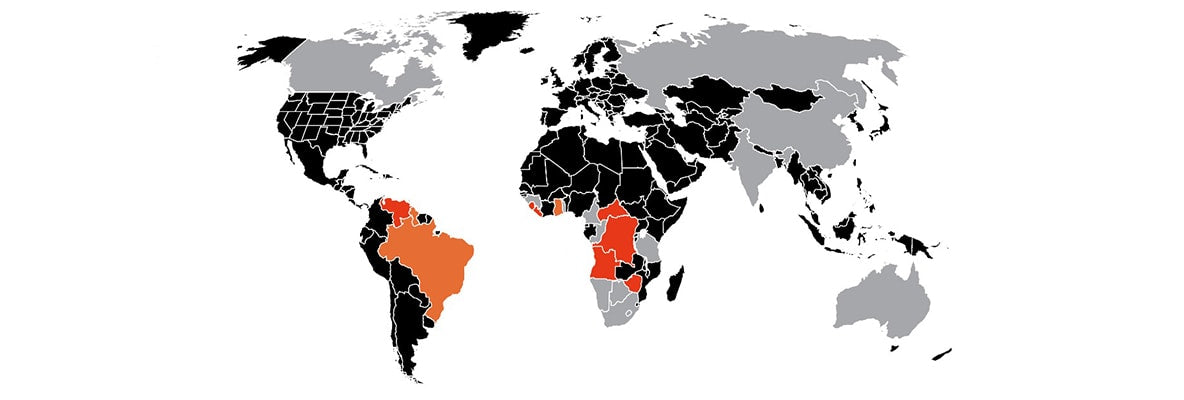
Diamonds have been discovered in countries such as Russia, Botswana, Canada, Angola, South Africa, Namibia, Australia, Zimbabwe and even in Guyana, India and Brazil. The top diamond mines in the world are responsible for more than 90% of the diamonds produced, with the other countries accounting for just 10% of the diamonds in the world. The top six countries are Russia, Botswana, Canada, Angola, South Africa and Namibia.
Russian Diamonds
Russia developed its diamond industry in order to fulfill its need for industrial supplies and equipment following World War II. Certain locations in Siberia exhibited certain characteristics similar to the carbon rich environment in South Africa that were rich with diamond deposits. The commercial sale and export of diamonds began in Russia in the 1960s. Russia continues to be the leader in the production of diamonds in terms of both sheer carat volume and even by dollar value. They have more than twelve functional open pit diamond mines.This position is not likely to change in the near future as Russia holds diamond reserves of more than 1 billion carats. It is not possible to tell the origin of a mined diamond by simply looking at it or even by inspecting its chemical composition. One way of identifying a Russian diamond is by having a relationship with a trusted supplier that can provide you with the origin information.
Canadian Diamonds
Canada is one of the newest players in the diamond industry. Canada began producing diamonds in the early 1990s. Most of its mines are located in the barren lands which can be found in the northern arctic regions of Canada. Many of the larger deposits can be found miles and miles below the ocean floor at the bottom of lakes. Canada has the distinction of being the world's third top producer of diamonds in terms of sheer dollar value. The prospects for Canada's increase in the amount of diamonds they produce look very positive as evidence suggests that they have much more deposits in different regions in huge expanses. A lot of these regions are yet to be explored and developed and there are even two huge, new projects set to begin. Canadian diamonds are similar to other diamonds in terms of their color, cut, carat and clarity.
Diamonds in the USA
The USA is one of the largest consumers of diamonds in the world, but very few diamonds mine's exist in the USA. In fact, only one working mine, which is called the Crater of Diamonds, located in Murfreesboro, Pike County, Arkansas. This is now a tourist attraction operated by the state, tourists and visitors alike can pay a fee to mine for diamonds and they can keep any Diamond they find. This mine produces a few hundred carats of diamonds annually, a small number in comparison to the total number of diamonds produced each year worldwide.
African Diamonds
Africa is blessed with vast expanses of diamond deposits all across its landscape. Currently there are 15 countries diamond producing countries in Africa. These are South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Ghana, Angola, Namibia, Congo, Guinea, Liberia, Lesotho, CAR, Tanzania, Sierra Leone and Togo. The largest producers of African diamonds are Botswana, South Africa, Angola, Namibia and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Although diamonds are available in many African countries, With Clarity ensures that they source diamonds that can only be found in conflict-free mines that adhere to strict ethical standards.
Price Differences
Diamond prices are determined by diamond suppliers and cutters. Typically, diamond cutters determine the prices of their diamond based on market values and supply and demand availability. Diamond prices do not fluctuate very heavily. If a diamond is severely underpriced, there may be a reason for this that pertains to it’s clarity, inclusions or color. Be sure to check all the diamond characteristics and comparing diamond prices before making your final selection. The value of all diamonds is ascertained by the 4 C's cut, color, clarity and carat. Diamonds from all over the world bear the same characteristics and are valued by the same four qualities. With Clarity works to ensure that all diamond supplier partners that we work with strict ethical standards. We aim to offer over 100,000 quality diamonds at reasonable wholesaler prices.
FAQs
What are ethically sourced diamonds?
Ethically sourced diamonds are diamonds obtained through responsible practices that consider human rights, environmental impact, and social welfare. Initiatives like the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme aim to prevent the trade of conflict diamonds.
Where are lab diamonds made?
Lab diamonds, also known as synthetic or cultured diamonds, are made in laboratories using high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) methods. These labs can be found in various countries around the world. Some prominent countries known for producing lab diamonds include the United States, Russia, China, India, Singapore, and several European countries.
Where are diamond mines located?
Diamond mines are located in various countries worldwide. Africa is a significant source of diamonds, with notable diamond mines found in Botswana, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and South Africa. Other regions known for diamond mining include Russia, which has extensive diamond deposits in Siberia and the Arkhangelsk region, as well as Canada, where diamond mines are located in the Northwest Territories. Additionally, Australia, Angola, Namibia, and Brazil also have diamond mining operations
How are lab grown diamonds created?
Lab-grown diamonds are created through two methods: high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). HPHT applies extreme pressure and temperature to a diamond seed, while CVD deposits carbon atoms layer by layer on a seed. Both methods replicate natural diamond formation, resulting in lab-grown diamonds with identical properties to natural diamonds.









