Real vs. Fake Diamonds: How to Tell If a Diamond Is Real

Imagine this scenario: Your beloved grandmother left you her jewelry box full of beautiful necklaces, earrings and brooches — and a few loose diamonds sitting in the bottom. She never mentioned these gemstones to you, so are they real diamonds?
The popularity — and price — of diamonds has inspired a whole industry of copycat gemstones (like cubic zirconia) designed to mimic the real things. The problem? It's usually difficult to tell if a diamond is fake or real just by looking at it. Luckily, there are multiple ways to find out the truth.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
How to Tell if a Diamond is Real or Not
You have two options when it comes to determining real diamonds vs fake diamonds. The first option is to enlist the help of an expert who can do a diamond test using professional equipment. Or two, if you don't want to use a professional, you can use a few at-home methods to figure out if your loose diamonds are real or fake.
How to Tell if a Diamond is Real at Home
While at-home methods for evaluating real vs. fake diamonds aren't absolutely foolproof, they are surprisingly accurate. All you need is a couple of household items.
The Sandpaper Test
This is an extremely easy diamond test because all you need is sandpaper (and a bit of elbow grease). Simply rub the gritty side of the sandpaper against the stone. Don't worry, the grit on sandpaper usually has a hardness between 7 and 9 on the Mohs scale. Diamonds are one of the world's hardest materials, so a real diamond won't be affected by the sandpaper, and should remain in perfect condition. However, if it's some type of fake diamond, then it will scratch.
The Read-Through Test
The read-through test is exactly what it sounds like: a diamond test where you attempt to read text through the diamond. Any diamond that is unmounted in a setting or piece of jewelry — also known as loose diamonds — can be tested this way. Follow these steps for the read-through test:
- Get a sheet of paper with plain black text on it.
- Turn the diamond upside down.
- Look through the upturned diamond to read the words on paper.
Note, it's impossible to read through a real diamond, but fake diamonds will allow you make out the words printed on the page.
The Sparkle Test
The way a stone reflects and refracts light is a good indication of its authenticity. The at-home sparkle test is a visual inspection of the stone's behavior in the light. A stone's natural light refraction cannot be altered, so the light refraction, — or lack thereof — of a gem is typically accurate. Synthetic or fake stones, sparkle less than real, or mined diamonds.
With light reflection, look for shades of gray. Synthetic stones, such as cubic zirconia, sparkle with more iridescent colors. Natural diamonds reflect light in more grayish hues. So, if yours is a stone of many colors, it's probably synthetic.
The Heat Test
To properly conduct the heat test, expose a loose gemstone to an open — but controlled — flame (like from a lighter), for about 30 to 45 seconds. Be careful with your fingers, and try to hold the stone with a pair of tweezers with a rubber base so there's no risk of getting a burn. Immediately after heating, put the gem into a container of cool water.
Why this method works: Diamonds conduct heat well and diffuse it evenly throughout the stone, while fake ones can't withstand heat. That said, the extreme heat and sudden switch to the cool water will ruin anything other than real diamonds, so don't do this home test unless you're willing to ruin a fake diamond.
On the other hand, if it turns out that your loose diamond is real, you can rest assured that it can stand up to any task you will put it with your unique lifestyle. You saw it with your own eyes, so you'll enjoy and appreciate the gem that much more.
Real diamonds vs. Lab-created Diamonds
Contrary to popular belief, lab-created diamonds aren't fake diamonds, they're just made in different settings. That said, there are still some minor differences between the two that you should be aware of while researching.
While real diamonds are mined from the earth, lab-created diamonds are made using techniques known as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or High-Pressure Crystal Formation (HPHT). To create the diamonds, carbon atoms are extracted from high-pressure vapor in a chamber. This process creates the diamond layer by layer over time — typically three months, though it can take longer. Real diamonds, on the other hand, can take thousands of years to form in the Earth.
Diamonds vs Moissanite
Whereas moissanite is not a lab-grown diamond. Moissanite was first discovered in the late 1800s in a meteor by Henri Moissan (hence the name). Moissan first assumed the clear particles were diamonds, but later discovered that these gemstones are not made from carbon, but silicon carbide.
While moissanite is a naturally occuring substance, it's difficult to find. So the majority of today's moissanite stones are created in labs. They're almost identical to diamonds, but there are a few big differences.
One of the most easily identified differences between moissanite stones and authentic diamonds is the color. The colors of natural diamonds are also more saturated than that of moissanite stones, which tend to appear to change colors as it disperses light throughout the gem. Although both produce stones that are yellow, clear or green, those with naturally red, blue, brown, black or purple tinted stones are likely in the diamond category.
Gemstone weight will also tell you whether you're dealing with a diamond or moissanite. Moissanite stones weigh less than their diamond counter parts, no matter how similar or exact their physical shape is. This is a harder quality to assess yourself, unless you happen to have professional jewel equipment at home, unless you're especially sensitive to the weight differences of two similar objects.
How to Tell the Difference Between Diamonds and White Sapphires
Comparing white sapphire gemstones to natural diamonds is more difficult to do on your own because they're typically similar in size, color purity, and saturation. They're also similar in strength and solidity. In fact, the only stone harder than white sapphires are natural diamonds, and it's a very close-call.
The differences lie deeper than the surface. For example, white sapphires form as corundum-based, hexagon-shaped crystal chunks. While carbon forms diamonds in crystal pieces that are square, or cubed. The different shapes and minerals affect both gemstones' facet shape and arrangement during development, creating different light reflection and refraction patterns.
Another difference between white sapphires and diamonds is purity. White sapphires are considered completely pure, period. Sapphires form in a variety of colors, but white ones have zero traces of other colors or murkiness. Moreover, they tend to either be 100 percent white, or a colored sapphire separate from the white sapphire. Clear, colorless diamonds are rarely truly pure and perfect, and some flawless diamonds have traces of other colors.
How to Check if a Mounted Diamond is a Real Diamond
If you have a diamond that is already placed in an engagement ring, this is a good indicator of whether it's fake or real.
To determine real vs. fake diamonds, first carefully examine the type of setting and mount that is used. Since real diamonds (whether mined or lab diamonds) tend to have a larger price tag, you won't find them set in cheap metals. A real diamond will typically only be set in metals such as white gold, yellow gold, rose gold, or platinum.
In order to tell what type of setting it is, look inside the ring's center for markings. For example, if you see the notes 10KT, 14KT or 18KT, those refer to the type of gold that is used. If you see the letters PT or Plat, those refer to the metal platinum. Also, if you see any numbers such as 585, 770, 900, or 950, those could indicate gold or platinum too. If you don't see any of the above markings, but you see the letters “C.Z.,” that means the gemstone is a cubic zirconia (a fake diamond).
How to Know if a Diamond is Real: Ask a professional
If you don't have time to do any of the at-home diamond tests — or if you don't trust yourself and want a second opinion — the best thing to do would be to take your stone to a qualified gemologist.
It's important to understand that not all jewelers are gemologists. Most of the time, they are salespeople, and don't have any of the education certified gemologists do. If you do go to a jewelry store, simply ask if they have any qualified gemologists who can help you, or if they can refer you to a reputable gemologist in town who knows about diamonds. Here at With Clarity, we have expert gemologists on staff who can assist you at any time. Consider them your trusty guide through our extensive database of diamonds and colored gemstones. They know which gemstone or diamond shape and weight will suit your tastes and budget, without sacrificing beauty in your stone. Our gemologists also make no commission off of their sales--so you know they're genuinely here help you, not just to make a sale.
If you take your diamond to a qualified gemologist, they won't just do the simple tests that you can do yourself at home. They have a few expert methods and tests they will perform in order to determine whether the diamond is real or fake. And lastly, you wouldn't have to risk damaging your gemstone.
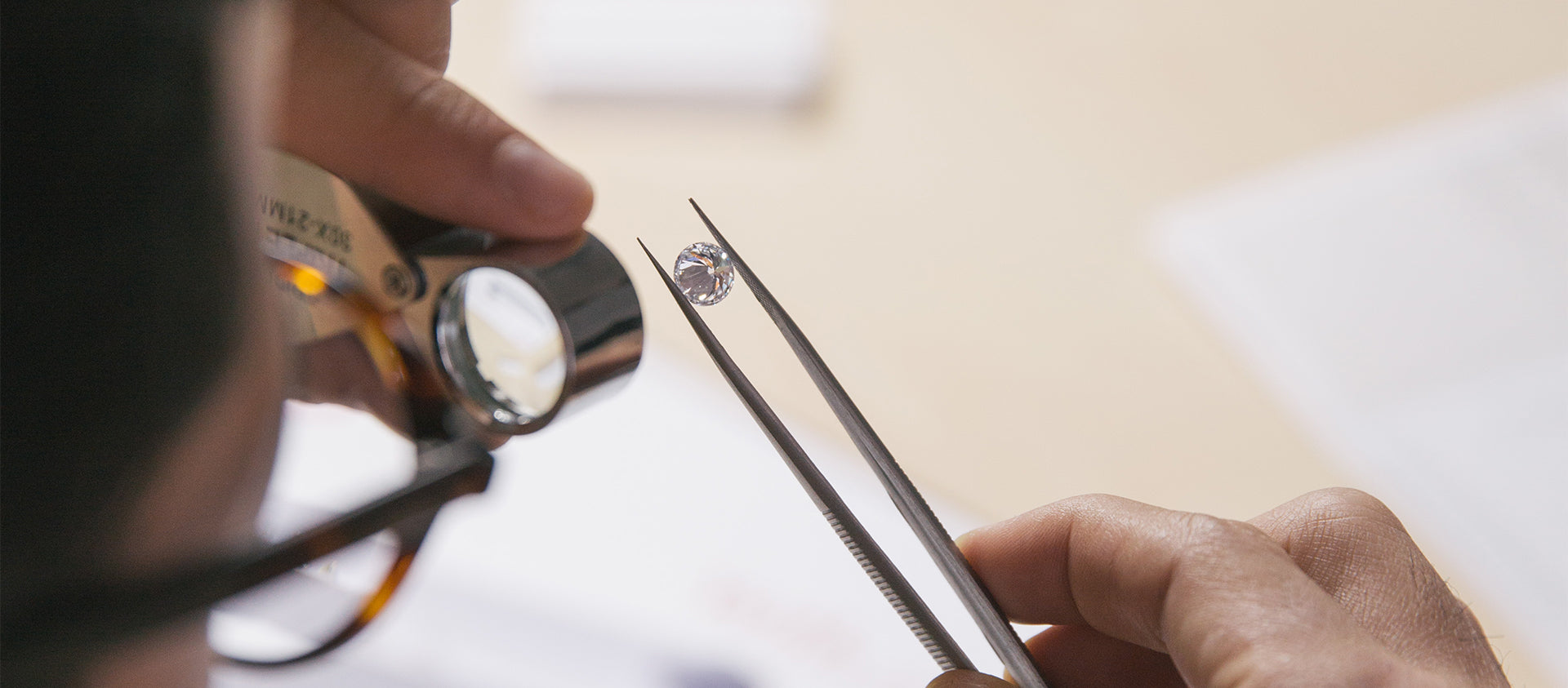
Diamond testing with a loupe
A loupe is a magnifying glass used for diamonds and gemstones. Professionals will look through the loupe for any blemishes and/or imperfections within the diamond. A fake diamond will typically not have inclusions, but a real diamond usually has small imperfections that are called inclusions.
The diamond tester tool
Also known as the Thermal Conductivity Probe, this diamond lighter test is used to determine the thermal conductivity of a gemstone. Real diamonds will disperse heat rapidly after being warmed, whereas fake diamonds will disperse heat at a slower rate.
High-Profile Weighing
This is the use of a fine tuned scale for measuring small differences in weight. With this scale, gemologists can use 1200x magnification on a power microscope to examine the stone in detail or conduct X-ray examinations to determine whether a diamond is fake or real.
The Final Word on the Real vs. Fake Diamond Debate
The best way to prevent any doubt about your diamond or stone is to verify the authenticity of the stone before purchasing and only purchase from a place that you trust. Any of these methods can help you determine whether a diamond is fake or real. However, always be sure to have a certified gemologist — like the experts at With Clarity — check your loose diamonds. You can conduct tests at home, but never rely on them to make any decisions about the diamond.
Expert Buying Tips
Try and maximize on the cut score and grade of the diamond. This represents the sparkle of the diamond and can help mask (or make up for) lower clarity grades, color tints, or smaller than desired carat weights. You may find value in a "Very Good" cut diamond that have most of the technical aspects of a Excellent cut diamond, but missed the cut off by a technicality such as a thick girdle or larger table facet.









